Flexible PCBs Suitable for High-Speed
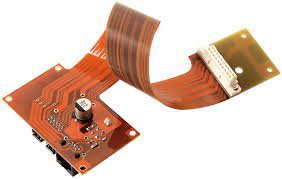
Whether they are used for mobile phones, tablets, wearables or automotive devices, flexible PCBs reduce weight and improve design by eliminating the need for wires and connectors. They are also highly durable and can withstand vibrations, harsh environments and temperature changes. These benefits make them ideal for high-speed applications. But are flexible pcb suitable for these applications? The answer depends on the design and fabrication process.
The first step is the preparation of the flex substrate. This consists of an epoxy or polyimide film that is usually a few mils thick. Conductive material traces are then etched on the substrate in as many layers as required by the PCB layout. After the copper has been etched, the flex is coated with an inert material to protect it from contamination and moisture. Finally, the flex is laminated with a coverlay to insulate and protect it from corrosion and damage.
One of the biggest challenges for a designer is to ensure that the flex is resilient enough to withstand the stresses and strains it will be subjected to. This requires careful consideration of the flex material choice and the thickness of the copper traces. It is important to use thinner traces wherever possible to increase flexibility and decrease the chance of cracking during bending. Additionally, the flex should be designed with a gradual change in width rather than using a sharp change. This will increase the stress resistance and allow for a smoother transition to the flex substrate.
Are Flexible PCBs Suitable for High-Speed Applications?
When designing a flex circuit, it is also important to consider the substrate material and its dielectric constant and loss tangent. The dielectric constant affects how quickly the signal travels on the flex and can cause delays and skew between adjacent traces. The loss tangent is the energy that the signal loses in the substrate material, and lower values will mean less attenuation and less risk of data errors.
Another important aspect of flex PCBs is the way that they are plated and fabricated. The etching and copper filling processes are the same as those for rigid boards, but the copper is exposed on all sides of the board. In addition, the flex is plated with a through-hole plating technique that allows for easy component placement.
Despite these additional steps, the production process is much faster for flex PCBs than rigid ones. This is due to the fact that the flex is thinner and more resilient, and it is easier for the copper to be cut into small sections. The etching and copper-filling process is also simpler, which means that the entire manufacturing cycle is faster.
The scalability of flex PCBs makes them ideal for complex 3D designs and allows them to be used in a wide variety of industry sectors. They are especially popular in consumer electronics and automobiles because they can help reduce the size of the device while still containing the necessary functionality. They are also well-suited to aerospace applications because of their ability to withstand high-speed vibrations, temperature fluctuations and pressure.